(LINKS TO PAST FOSSIL FRIDAYS)
Community
College (LRCCD)
Geology & Earth Science Instructor: Arthur
Reed, P.G.
Happy Fossil Friday!
Friday September 17, 2021
Egyptian
scientists have published their findings of the fossil of a 4-legged whale
found southwest of Cairo in the Egyptian desert. It was discovered in 2008 but not studied
until recently. This helps fill in the gap in understanding how whales evolved
from land mammals back to sea creatures (to sea mammals). One story of this finding is below, along
with a couple videos that should help you understand.
Scientists
Discover Fossil of A 4-Legged Whale With A Raptor-Like
Eating Style
August
27, 2021
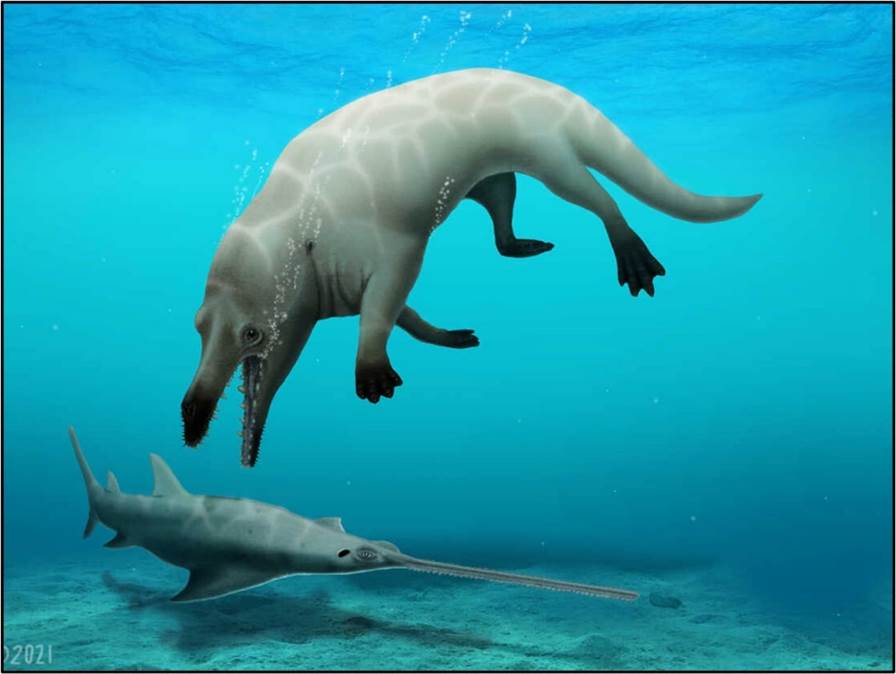

A group of scientists have
discovered a fossil of a now-extinct whale with four legs. This visual
reconstruction shows Phiomicetus anubis preying on a sawfish.
Robert W. Boessenecker
We regret to
inform you that your nightmares are about to get worse.
A team led by
Egyptian scientists have
dug up a 43 million-year-old fossil in the Sahara Desert in Egypt of a
now-extinct amphibious four-legged whale.
That's right,
folks — a whale with legs.
The authors of
the study say that this creature had "unique features of the skull"
and that its "mandible suggest a capacity for more efficient oral
mechanical processing."
Discovery location in Egypt
In
other words, these walking whales had a "strong raptorial feeding
style."
"We
discovered how fierce and deadly its powerful jaws are capable of tearing a
wide range of prey ... this whale was a god of death to most of the animals
that lived in its area," Abdullah Gohar, one of the scientists, told Insider.
The
new whale is called Phiomicetus anubis, which the scientists named
in part after Anubis, the canine-headed Egyptian god associated with
mummification and the afterlife. It was likely a top predator at the time, similar to what a killer whale is today.
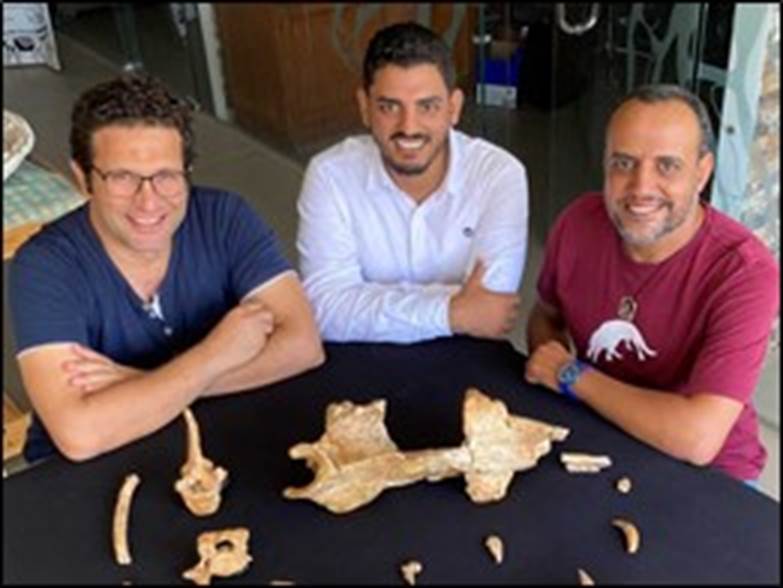

Study authors Mohamed Sameh
(from left), Abdullah Gohar and Hesham Sallam surround the holotype fossils of
the new whale, Phiomicetus anubis, at Mansoura University Vertebrate
Paleontology center.
Abdullah Gohar
Whales,
it turns out, used to be "herbivorous, deer-like terrestrial
mammals," the scientists write. Over the span of about 10 million years,
whales turned into carnivorous creatures in the ocean. The discovery of the
four-legged creature is part of that evolution.
VIDEOS:
One-minute
video story by ‘Swarajya’ (a periodical based in India)
Three-minute
video by Egyptian researcher Hesham Sellam
Very
good eleven-minute video on whale evolution from land to sea (but does not include the discovery
of Phiomicetus anubis.